In the wake of Aaron Bushnell’s self-immolation, Ann Wright recalls other suicides committed in protest against U.S. policies, including by five Americans opposed to the U.S. war in Vietnam.
Buddhist monk Thich Quang Duc burning himself to death in Saigon in protest of persecution of Buddhists by the South Vietnam government. (Associated Press, Public Domain/Wikimedia Commons)
 Four years ago in 2018, after returning from a Veterans For Peace trip to Vietnam, I wrote an article called “Why Would Anyone Kill One’s Self In an Attempt to Stop A War?”
Four years ago in 2018, after returning from a Veterans For Peace trip to Vietnam, I wrote an article called “Why Would Anyone Kill One’s Self In an Attempt to Stop A War?”
Now, four years later, in the past three months, two people in the United States have taken or risked taking their own lives in an attempt to change U.S. policies on Palestine, call for a cease-fire and stop U.S. funding to the State of Israel to be used in the Israeli genocide of Gaza.
A still-unidentified woman, wrapped in a Palestinian flag, set herself on fire in front of the Israeli consulate in Atlanta on Dec. 1, 2023. Three months later authorities have yet to release the name of the woman. Her condition was unknown as of mid-December.
On Sunday, active-duty U.S. Air Force member Aaron Bushnell set himself on fire at the Israeli Embassy in Washington, D.C., while he was stating, “Free Palestine and stop the genocide.” Bushnell died from his injuries.
As I mentioned in the article in 2018, many in the U.S. admire young men and women who join the military and profess to be willing to give up their lives for whatever the U.S. politicians or government decide is best for another country — “freedom and democracy” for those who don’t have the U.S. version of it, or overthrowing self-rule that is not compatible with the U.S. administration’s view.
Actual U.S. national security seldom has anything to do with U.S. invasions and occupations of other countries.
But, what about a private citizen giving up his or her life to try to stop the politicians or government from deciding what is best for other countries? Could a “mere” citizen be so concerned about politicians’ or government actions that she or he is willing to die to bring public attention to those actions?
One well-known and several little-known actions of private citizens from five decades ago provide us with the answers.
While on a Veterans for Peace trip to Vietnam in 2014 and while on another VFP delegation in March 2018, our delegation saw the iconic photo of Buddhist monk Thich Quang Duc who set himself on fire in June 1963 on a busy street in Saigon to protest the Diem regime’s crackdown on Buddhists during the early days of the American war on Vietnam. That photo is seared into our collective memories.
The photo shows hundreds of monks surrounding the square to keep the police out so that Quang Duc could complete his sacrifice. The self-immolation became a turning point in the Buddhist crisis and a pivotal act in the collapse of the Diem regime in the early days of the American war on Vietnam.
Americans Who Self-Immolated During Vietnam War
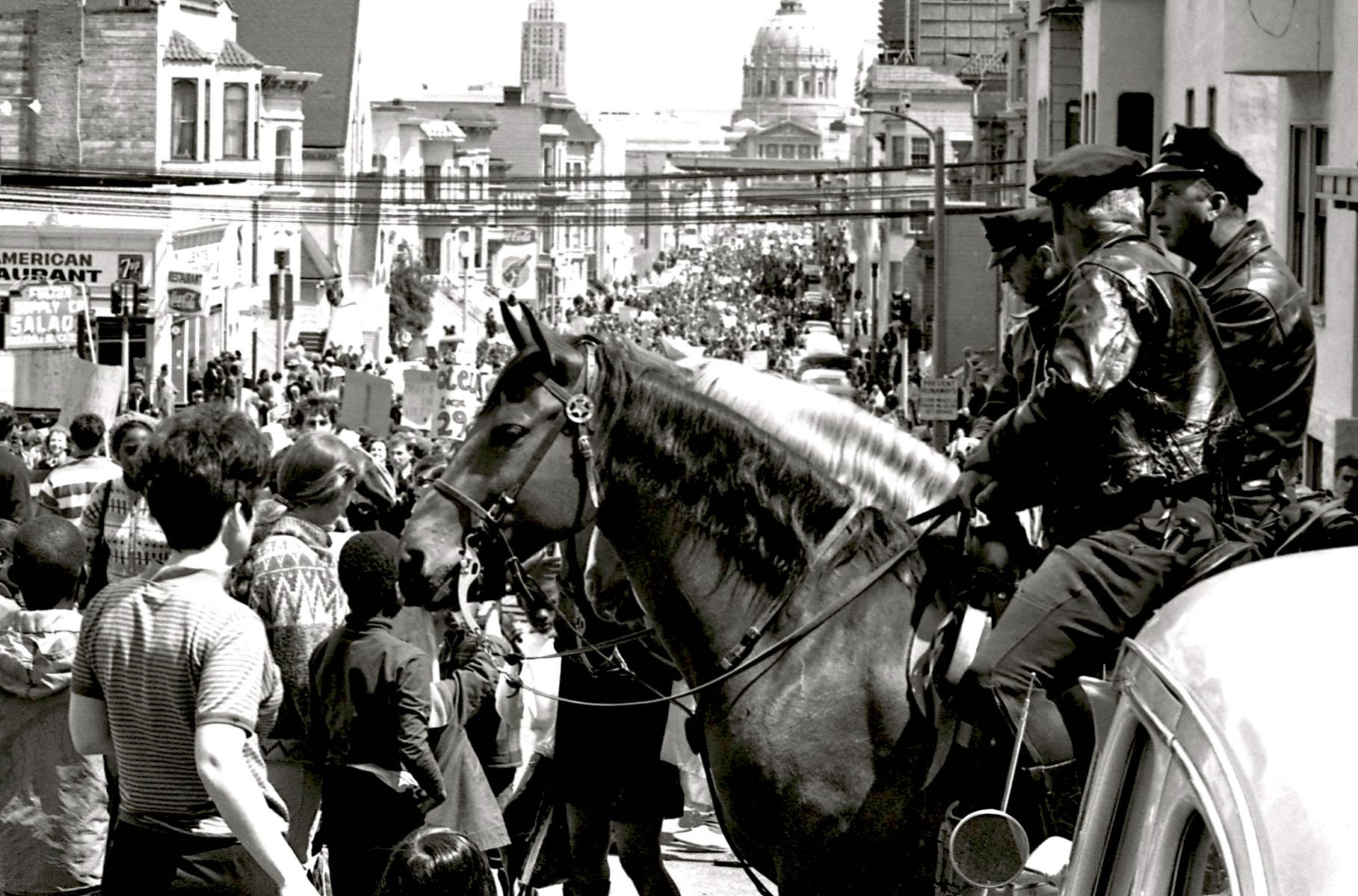

Mounted policemen at protest march against the war in Vietnam in San Francisco, April 15, 1967. (BeenAroundAWhile, Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0)
But, did you know that several Americans also set themselves on fire to attempt to end U.S. military actions during those turbulent war years in the 1960s?
I didn’t, until our VFP delegation saw the portraits displayed of five Americans who gave their lives to protest American involvement in Vietnam, among other international persons who are revered in Vietnamese history, at the Vietnam-USA Friendship Society in Hanoi.
Though these Americans have fallen into oblivion in their own nation, they are well-known martyrs in Vietnam, 50 years later.
Our 2014 delegation of 17 — six Vietnam veterans, three Vietnam-era vets, one Iraq-era vet and seven civilian peace activists — with four Veterans for Peace members who live in Vietnam, met with members of the Vietnam-USA Friendship Society at their headquarters in Hanoi.
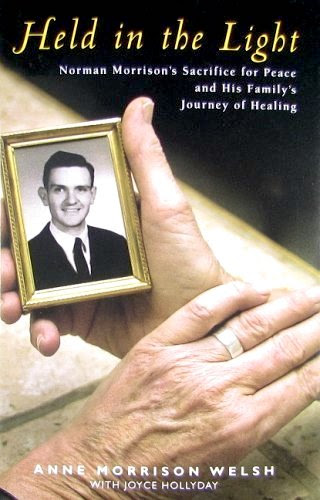
I returned to Vietnam in March 2018 with another Veterans for Peace delegation. After seeing one particular portrait again — that of Norman Morrison — I decided to write about these Americans who were willing to end their own lives in an attempt to stop the American war on the Vietnamese people.
What distinguished these Americans to the Vietnamese was that, as American soldiers were killing Vietnamese, there were American citizens who ended their own lives in order to try to bring the terror of invasion and occupation for Vietnamese citizens to the American public through the horror of their own deaths.
The first person in the United States to die of self-immolation in opposition to the war on Vietnam was 82-year-old Quaker Alice Herz who lived in Detroit. She set herself on fire on a Detroit street on March 16, 1965. Before she died of her burns 10 days later, Alice said she set herself on fire to protest “the arms race and a president using his high office to wipe out small nations.”
Six months later on Nov. 2, 1965, Norman Morrison, a 31-year-old Quaker from Baltimore, a father of three young children, died of self-immolation at the Pentagon. Morrison felt that traditional protests against the war had done little to end it and decided that setting himself on fire at the Pentagon might mobilize enough people to force the United States government to abandon its involvement in Vietnam.
Morrison’s choice to self-immolate was particularly symbolic in that it followed President Lyndon Johnson’s controversial decision to authorize the use of napalm in Vietnam, a burning gel that sticks to the skin and melts the flesh.
Apparently, unbeknownst to Morrison, he chose to set himself on fire beneath the Pentagon window of then-Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara.
Thirty years later in his 1995 memoir, In Retrospect: The Tragedy in Lessons of Vietnam, McNamara remembered Morrison’s death:
“Antiwar protests had been sporadic and limited up to this time and had not compelled attention. Then came the afternoon of November 2, 1965. At twilight that day, a young Quaker named Norman R. Morrison, father of three and an officer of the Stony Run Friends Meeting in Baltimore, burned himself to death within 40 feet of my Pentagon window. Morrison’s death was a tragedy not only for his family but also for me and the country. It was an outcry against the killing that was destroying the lives of so many Vietnamese and American youth.
I reacted to the horror of his action by bottling up my emotions and avoided talking about them with anyone — even with my family. I knew Marge and our three children shared many of Morrison’s feelings about the war. And I believed I understood and shared some of his thoughts. The episode created tension at home that only deepened as the criticism of the war continued to grow.”
Before his memoir In Retrospect was published, in a 1992 article in Newsweek, McNamara had listed people or events that had had an impact on his questioning of the war. One of those events McNamara identified as “the death of a young Quaker.”
One week after Morrison’s death, Roger LaPorte, 22, a Catholic Worker, became the third war protester to take his own life. He died of burns suffered through self-immolation on Nov. 9, 1965 on the United Nations Plaza in New York City [that news was eclipsed by the Great Northeastern Blackout that night]. He left a note that read, “I am against war, all wars. I did this as a religious act.”
The three protest deaths in 1965 mobilized the anti-war community to begin weekly vigils at the White House and Congress. And every week, Quakers were arrested on the steps of the Capitol as they read the names of the American dead, according to David Hartsough, one of the delegates on our 2014 VFP trip.
Hartsough, who participated in anti-war vigils 50 years earlier, described how they convinced some members of Congress to join them. Rep. George Brown (D-CA) became the first member of Congress to do so. After the Quakers were arrested and jailed for reading the names of the war dead, Brown would continue to read the names, enjoying congressional immunity from arrest.
Two years later, on Oct. 15, 1967, Florence Beaumont, a 56-year-old Unitarian mother of two, set herself on fire in front of the Federal Building in Los Angeles. Her husband George later said,
“Florence had a deep feeling against the slaughter in Vietnam… She was a perfectly normal, dedicated person, and felt she had to do this just like those who burned themselves in Vietnam. The barbarous napalm that burns the bodies of the Vietnamese children has seared the souls of all who, like Florence Beaumont, do not have ice water for blood, stones for hearts. The match that Florence used to touch off her gasoline-soaked clothing has lighted a fire that will not go out — ever — a fire under us complacent, smug fat cats so damned secure in our ivory towers 9,000 miles from exploding napalm, and THAT, we are sure, is the purpose of her act.”
Three years later, on May 10, 1970, 23-year-old George Winne, Jr., son of a Navy captain and a student at the University of California, San Diego, set himself on fire on the university’s Revelle Plaza next to a sign that said “In God’s name, end this war.”
 Winne’s death came just six days after the Ohio National Guard fired into a crowd of Kent State University student protesters, killing four and wounding nine, during the largest wave of protests in the history of American higher education.
Winne’s death came just six days after the Ohio National Guard fired into a crowd of Kent State University student protesters, killing four and wounding nine, during the largest wave of protests in the history of American higher education.
At our 2014 meeting at the Vietnam-USA Friendship Society office in Hanoi, David Hartsough presented Held in the Light, a book written by Ann Morrison, the widow of Norman Morrison, to Ambassador Chin, a retired Vietnamese ambassador to the United Nations and now an official of the Society. Hartsough also read a letter from Ann Morrison to the people of Vietnam.
Ambassador Chin responded by telling the group that the acts of Norman Morrison and other Americans in ending their lives are well remembered by the people of Vietnam.
He added that every Vietnamese school child learns a song and poem written by Vietnamese poet To Huu called “Emily, My Child” dedicated to the young daughter that Morrison was holding only moments before he set himself on fire at the Pentagon. The poem reminds Emily that her father died because he felt he had to object in the most visible way to the deaths of Vietnamese children at the hands of the United States government.
Sparking Revolutions
In other parts of the world, people have ended their lives to bring attention to special issues. The Arab Spring began on Dec. 17, 2010, with a 26-year-old street Tunisian vendor named Mohamed Bouazizi setting himself on fire after a policewoman confiscated his food street vending cart. He was the only breadwinner for his family and had to frequently bribe police in order to operate his cart.
His death sparked citizens throughout the Middle East to challenge their repressive governments. Some administrations were forced from power by the citizens, including Tunisian President Zine El Abidine Ben Ali, who had ruled with an iron fist for 23 years.
Ignored as Irrational Acts
In the United States, acts of conscience such as taking one’s own life for an issue of extraordinary importance to the individual are viewed as irrational and the government and media minimize their importance.
[Related: What Happened to the Global Uprisings of a Decade Ago?]
For this generation, while thousands of U.S. citizens are arrested and many serve time in county jails or federal prisons for protesting U.S. government policies, in April 2015, young Leo Thornton joined a small but important number of women and men who have chosen to publicly end their lives in hopes of bringing the attention of the American public to change specific U.S policies.
On April 13, 2015, Leo Thornton, 22 years old, committed suicide by gun on the West Lawn of the U.S. Capitol. He had tied to his wrist a placard that read “Tax the 1%.” Did his act of conscience have any effect on Washington — the White House or the U.S. Congress? Unfortunately, not.
The following week, the Republican-led House of Representatives passed legislation that would eliminate the estate tax applying only to the top 1 percent of estates. And no mention of Leo Thornton, and his decision to end his life over inequitable taxation, appeared in the media to remind us that he ended his life in opposition to another piece of favorable legislation for the rich.
Then years ago, in October 2013, 64-year-old Vietnam veteran John Constantino set himself on fire on the Washington, D.C., National Mall — again for something he believed in. An eyewitness to Constantino’s death said Constantino spoke about “voter rights” or “voting rights.” Another witness said he gave a “sharp salute” toward the Capitol before he lit himself on fire. A neighbor who was contacted by a local reporter said Constantino believed the government “doesn’t look out for us and they don’t care about anything but their own pockets.”
The media didn’t investigate any further the rationale for Constantino taking his own life in a public place in the nation’s capital.
Ann Wright served 29 years in the U.S. Army/Army Reserves and retired as a colonel. She was a U.S. diplomat for 16 years and served in U.S. embassies in Nicaragua, Grenada, Somalia, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Sierra Leone, Micronesia, Afghanistan and Mongolia. She resigned from the U.S. Diplomatic Corps 20 years ago in March 2003 in opposition to the U.S. war on Iraq. She is the co-author of Dissent: Voices of Conscience.
This article is from Common Dreams.
Post Disclaimer
Disclaimer: Killing Oneself to Try to Stop a War - Views expressed by writers in this section are their own and do not necessarily reflect Latheefarook.com point-of-view